Institutions
Hyanji Scaffold brings together a range of experienced researchers from Europe and China.
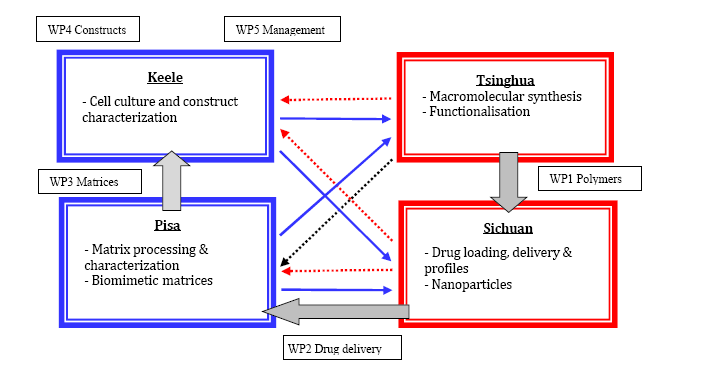
The four partners forming the Europe-China exchange bring complementary expertise, human resources, facilities and infrastructure with mutual benefit in knowledge integration and technology transfer. Tsinghua's contribution is in biosynthesis and applications of novel macromolecular materials. Sichuan has strength in formulation and toxicity tests. Pisa has well established infrastructure in polymer synthesis and characterization. Keele has strength in tissue engineering.
The four partner institutions, in alphabetical order, are:
Click on the names to read a summary of involvement in the HYANJI SCAFFOLD project. The relationship between the partners is summarised in the diagram below:
Keele University, United Kingdom
The Institute for Science & Technology in Medicine (ISTM) at Keele is a leading EU centre in tissue engineering especially of musculoskeletal tissues. It has a distinguished multidisciplinary team that covers molecular and cell biology, stem cells, bioreactors, surgery, biomaterials and nanotechnology. Keele is known for its success in translating biomedical research to the clinic and industry. Over the last decade, ISTM has scored the highest ratings in the UK’s research quality assessment exercises and has been involved in several European projects including Marie Curie training (ALEA JACTA), Network of Excellence (EXPERTISSUES), and NEST projects (MYJOINT). Collaborative research projects have included BITES, EUROCELL, CELL ENG and NESTING. Members of ISTM have collaborative research links with over 125 other institutions and companies spanning 35 countries throughout the world.
Keele will assess matrices, cytocompatibility, proliferation and differentiation, conducting functional cell (e.g. stem cells, chondrocytes, bone cells, and tendon cells). Dynamic cell culture using bioreactor and online monitoring (pH, O2 and CO2) will be used and data can be used for future in silico modelling.
Pisa University, Italy
The University of Pisa is one of the most renowned Italian universities. The Department of Chemistry and Industrial Chemistry has well established infrastructure in polymer synthesis and characterization. The Department has 80 staff members and 35 technical & administrative personnel.
The Pisa team will be involved (with other partners) in processing of polymers for the production of:
a) Polymeric scaffolds by means of computer-aided biomanufacturing and rapid prototyping technique, electrospinning from solution and melt materials,
b) Polymeric nanoparticles for the administration of bioactive agents as prepared according to proprietary methodologies developed in house.
Sichuan University, China.
Sichuan is the only State Key Laboratory of Drug Targeting and Drug Delivery System, in China. The College of Pharmacy was founded in 1932. The school takes an active part in international academic exchanges and cooperation—more than 200 staff members have been sent abroad. Reciprocally, more than 300 scholars and specialists from USA, Japan etc. have been received. The School has established a intercollegiate relationship with the School of Pharmaceutical Sciences of Kyoritsu University, Japan.
Sichuan has broad research on drug delivery systems, and will add this function to developed materials.
Tsinghua University, China.
Tsinghua University is among the top 5 Universities in China and the strongest team in polyhydroxyalkanoates tissue engineering application. The Department of Biological Sciences and Biotechnology (DBSB) was founded in 1926 and has been one of the earliest bases focusing on life science education and research in China.
The Tsinghua team will work on the biosynthesis of polyhydoxyalkanoates (PHA) and of hyaluronic acid by microorganisms under specific growth conditions to produce smart matrices. To be biomimetic, matrix should also have the function of storage and controlled release of bioactive elements, such as growth factors needed to enhance cell function and control differentiation.
Accordingly, together the partners will lead to faster and stronger progress in knowledge transfer and developing new smart tissue engineering systems. The partners are centres of excellence and are already involved in joint work with each other which enhances familiarity, efficiency and productivity in the current project. Keele and PISA are leaders in tissue engineering in EU while Sichuan and Tsinghua are leading centres in China. This consortium makes the necessary combination for long-lasting collaboration towards European excellence in this field and closing the current gap with Japan & the USA.

