Why use Problem-Based Learning for Sustainability Education?
Many educators believe that the ideal pedagogies for the development of sustainability literacy are those which enable students to develop practical problem solving skills in real-life sustainability contexts; pedagogies which are student-centred, active, experiential, collaborative, practical, contextual, skills-focused and problem-based. The broad area of 'sustainability' is ideally suited to PBL because the problems are complex, and their multidisciplinarity makes them well-suited to group-based exploration. A PBL approach provides genuine opportunities for students to tackle current sustainability issues within their immediate environment.
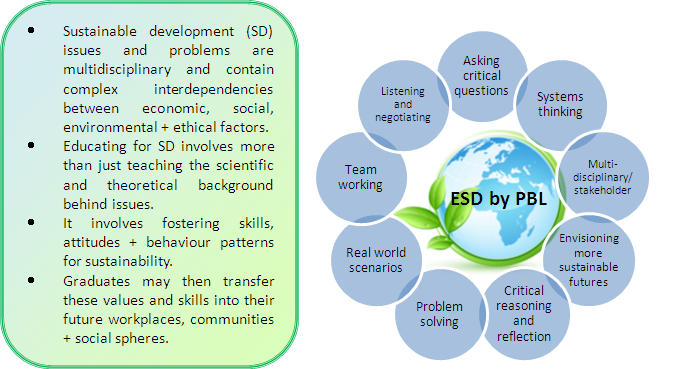
- The active and collaborative learning processes involved in PBL and the real world scenarios used are ideal for building such sustainability competencies and skills.
- Students are able to search for problem solutions and develop new skills through a holistic systems approach to sustainable development.
- Students are encouraged to cross disciplinary boundaries, consider multiple and international stakeholder views, exchange ideas, insights and knowledge and build a new collaborative level of understanding.
We believe that successful PBL is capable of providing deep and transformative sustainability education and developing the skills needed to ensure graduates become active agents of positive change for sustainable development.
PDF version available
This file may not be suitable for some users of assistive technology
Request an accessible format

